Gut viruses may help to alleviate stress, say researchers based at UCC
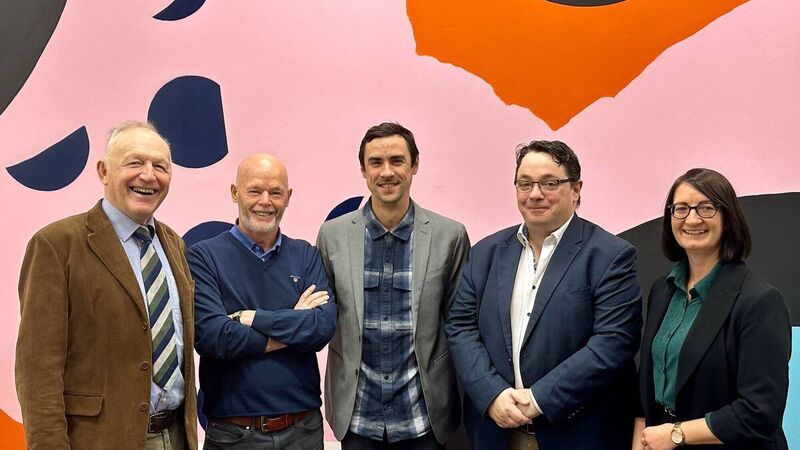

A world-first discovery on the role the human virome plays in stress management has taken place in APC Microbiome Ireland, a world leading SFI Research Centre based in University College Cork. First Author Dr Nathaniel Ritz is pictured with APC Operations Manager Dr Lorraine Draper who contributed to the research and Corresponding Authors Profs Ted Dinan, Colin Hill and John Cryan.
RESEARCHERS at APC Microbiome Ireland (APC), a Science Foundation Ireland research centre based at University College Cork, have made a discovery in the role the human virome plays in stress management.
The findings may help to develop treatments to reduce stress and stress-related disorders by targeting the virome, the vast community of viruses hosted by every human body.
One in eight people has a mental disorder, according to the World Health Organization, and stress-related psychiatric disorders, such as depression and anxiety, are prevalent and are significant societal burdens.
Although most people think of viruses as harmful (covid, influenza, the common cold), there are other viruses, known as bacteriophages, that infect bacteria, including pathogenic bacteria, and which can play a role in maintaining our health and well-being.
Over the past decade, a burgeoning field of research, studying the human microbiome, has demonstrated that the microbes in a person’s gut play a pivotal role in physical and mental health.
The composition of bacteria in the gut changes with stress and targeting these bacteria may alleviate stress, but, up to now, all the focus has been on bacteria.
As part of this new research, Professor John Cryan and colleagues teamed up with the bacteriophage laboratory of Professor Colin Hill, at APC, to decode the contribution of these gut viruses to stress.
Changes in virome composition
The study, published in Nature Microbiology, found that chronic stress led to changes in virome composition that were associated with behavioural, immune, and bacteriome alterations, supporting increasing evidence that brain-gut interactions play a key role in how stress is regulated.
An understanding of the biological consequences of chronic stress offers the potential to develop alternative, new therapies.
Next, a faecal virome transplant (FVT) — they harvested viruses from healthy animals prior to stress and returned then to the stressed gut — was able to exert remarkable outcomes in preventing stress-associated behavioural and physiological issues.
The research provides strong causal evidence that the viral component of the microbiome can be used to restore the microbiota-gut-brain axis during stress and a potential treatment strategy for stress-related psychopathologies.
Dr Nathaniel Ritz, first author on the study, said: “Although bacteria in the gut has been the subject of growing research, the way the virome interacts with bacteria, and how they affect stress-related health and disease status, is largely unexplored.
“Our research focuses on this and highlights a link between stress-related behaviours and the gut bacteriome and virome, which opens up the potential to target the virome to treat and reduce the effects of stress.”
Validation now needed in human studies
Prof Cryan said: “This important research is a step advancement in developing targeted virome therapies that reduce the effects of stress with safer therapeutic interventions, and points to the potential of further research on the dynamics of the microbiota-gut-brain axis to promote gut and brain health.”
He cautioned that “these are mice studies and validation in humans is now required to assess the potential of the FVT approach”.
The research may open the door for personalised-medicine approaches for stress-related disorders.
APC director Professor Paul Ross said: “I’d like to congratulate the APC teams involved. The virome is a nascent research area and we are excited at the huge potential there to develop therapeutics.
“To have established a tangible link with chronic stress, at this early stage, is a huge advancement and we look forward to deepening this research area.”








 App?
App?


